Non-urgent government operations are closed December 24 to January 1, reopening January 2. View available services during this period.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They do not take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: United Mexican States
Location: North America
Capital: Mexico City
Area: 1.97 million square km
Population: 112 million (2010 census
Ethnicity: Mexico enumerates people on whether or not they speak Spanish or indigenous languages. Mexico does not collect census data on ethnicity. In Mexico, the racial division is between the mestizo and indigenous populations.
Religion: The Mexican population is predominantly Catholic (84%) (2010 census).
Languages: Spanish is the official language. There are 62 indigenous languages spoken in Mexico as “national languages”. The greatest number of speakers is Nahuatl (1.5% of the population), followed by Yucatec Maya (0.8% of the population) (2010 census).
Founding Date: Mexico was the site of several advanced Amerindian civilizations, including Olmec, Maya, and Aztec. Mexico was conquered and colonized by Spain in the early 16th century. Administered as the Viceroyalty of New Spain for 3 centuries. Mexico achieved independence on September 16, 1810.
Administration: Mexico is a federal republic consisting of 31 states and 1 federal district.
School education
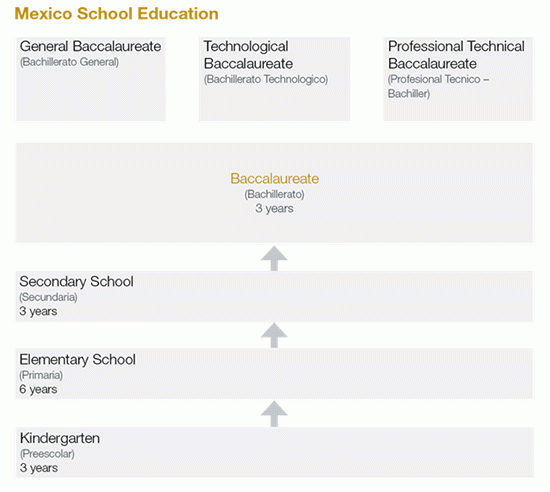
School education in Mexico is a total of 12 years, consisting of basic education (educación básica) and upper secondary education (educación media superior). Basic education includes 3 years of compulsory preschool (preescolar), 6 years of primary (primaria) (Grades 1 to 6), and 3 years of secondary (secundaria) (Grades 7 to 9) school. Upper secondary education covers a period of 3 years of schooling (Grades 10 to 12). The choices that students make in upper secondary school (general bachillerato / tecnologico bachillerato / professional tecnico bachiller) affect their higher education decisions and future employment. Students have to meet program and exit examination requirements in order to graduate and receive the Certificate of Baccalaureate (Certificado de Bachillerato).
Higher education overview
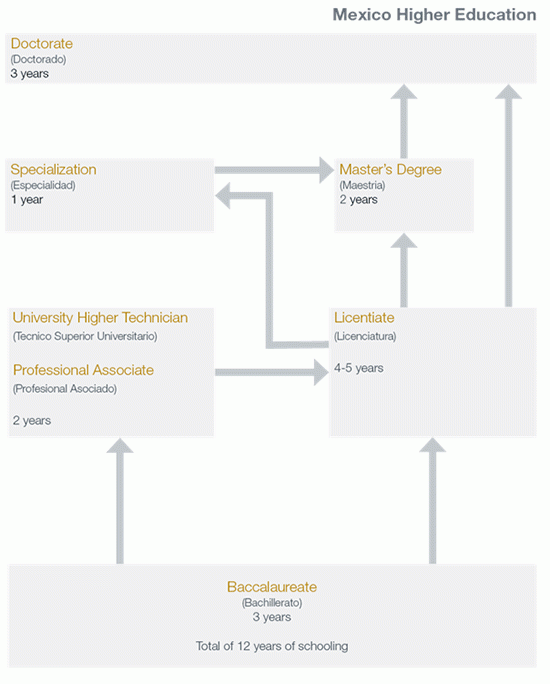
The Mexican higher education system includes 2 levels: undergraduate (pregrado) and graduate (posgrado). The undergraduate level comprises University Higher Technician (Técnico Superior Universitario) or Professional Associate (Profesional Asociado) and Licentiate (Licenciatura) programs. Graduate programs include Specialist (Especialización), Master (Maestría), and Doctoral (Doctorado) degrees.
University Higher Technician (Tecnico Superior Universitario) / Professional Associate (Profesional Asociado) programs are 2 years in length following an upper secondary school program. Graduates receive a Title of University Higher Technician (Título de Técnico Superior Universitario) or Title of Professional Associate (Título de Profesional Asociado).
A Licentiate (Licenciatura) degree involves 4 or 5 years of full-time study after a baccalaureate program. Study in medicine (medico) lasts for 6 years. Holders a Title of University Higher Technician / Professional Associate have the option to continue study in a licenciatura program. The final degree at a licentiate level is a Title of Licentiate (Título de Licenciado).
Specialization (Especialización) programs require a licentiate for admission. The program length is 1 year of full-time study. Completion of coursework is the basic requirement to earn a Diploma of Specialist (Diploma de Especialidad).
Master (Maestria) degrees involve 2 years of full-time study following a licentiate degree or specialist diploma program. A Master’s Degree (Grado de Maestría) is awarded to graduates.
The Doctoral (Doctorado) degree lasts for 3 or more years of full-time study following a master’s degree in a related field or 5 or more years following a licentiate degree. A Doctor’s Degree (Grado de Doctor) is the highest university credential in Mexico.
Technical education
Vocational and technical education prepares students for a professional role within industry. Technical Professional – Baccalaureate (Profesional Técnico – Bachiller) and Technological Baccalaureate (Bachillerato Tecnológico) programs are offered at the secondary level. These 3-year vocational and technical programs are designed to provide introductory knowledge and skills in an area of work. They also prepare students for further technical study at the undergraduate level. After successful completion of these programs, students are awarded the title of Technician (Técnico). The Technical Professional (Profesional Técnico) training stream also offers terminal programs, such as an Assistant Technician (Técnico Auxiliar), Basic Technician (Técnico Básico) or Professional Technician (Técnico Profesional).
Post-secondary programs resulting in the titles of University Higher Technician (Tecnico Superior Universitario) / Professional Associate (Profesional Asociado) involve 2 years of full-time study and allow graduates to enter certain professions such as engineering technology, dental hygiene, nursing, etc.
Institutions
There are 2 systems of higher education institutions: public (pública) and private (particular). Both public and private higher education institutions offer all types of degrees in all disciplines.
The public system includes federal and state higher education institutions, many of which have been awarded the status of ‘autonomous’. Autonomous institutions have the word autónoma in their name. They have autonomy over management, budgeting, and curricular content. Non-autonomous higher education institutions follow study requirements of the Secretariat of Public Education (Secretaria de Educación Pública, SEP) or state departments of education.
The Mexican public higher education institutions consist of the following types: federal institutions (instituciones federativas), state universities (universidades estatales), intercultural universities (universidades interculturales), technological institutes (institutos tecnológicos), technological universities (universidades tecnológicas), polytechnic universities (universidades politécnicas), and normal and higher normal schools (escuelas normales / escuelas normales superiores). All programs offered at public institutions are recognized and possess the status of official validity of studies (validez official de estudios).
The programs of study of private higher education institutions are supervised by either SEP or state departments of education or by public autonomous universities. To be officially recognized, private higher education institutions required to be approved by the SEP and to obtain the Recognition of Official Validity of Studies (Reconocimiento de Validez Oficial de Estudios, RVOE) for each program. The recognition status of a private higher education institution can be verified through the RVOE website.
The accreditation system is voluntary in Mexico and is maintained by the Higher Education Accreditation Council (Consejo para la Acreditación de la Educación Superior, COPAES).
Credential comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Bachillerato (Baccalaureate) | Completion of Grade 9: Certificado de Estudios de Educacion Secundaria (Certificate of Secondary Education) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| Titulo de Maestro / Profesor de Educación Preescolar (Title of Preschool Teacher) Titulo de Maestro / Profesor de Educación Primaria (Title of Primary School Teacher) | Completion of Grade 9: Certificado de Estudios de Educacion Secundaria (Certificate of Secondary Education) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma, including specialized training in teacher education. |
| Título de Técnico Superior Universitario (Title of Higher University Technician) / Título de Profesional Asociado (Title of Professional Associate) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 2-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| Título de (Title of) Título de Licenciado (Title of Licentiate) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) Título de Técnico Superior Universitario (Title of Higher University Technician) / Título de Profesional Asociado (Title of Professional Associate): advanced standing | 4 or 5 years or 2 or 3 years after a Título de Técnico Superior Universitario / Título de Profesional Asociado | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Título de Licenciado en Medico Cirujano (Title of Licentiate in Medicine and Surgery) Licenciatura en Medicina General (Licentiate in General Medicine) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) | 6 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine. |
| Licenciatura en Cirujano Dentista (Licentiate in Dental Surgery) Licenciatura en Odontologia (Licentiate in Dentistry) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in dentistry. |
| Título de Licenciado en Medicina Veterinaria y Zootecnia (Title of Licentiate in Veterinary Medicine and Animal Husbandry) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in veterinary medicine. |
| Título de Licenciado en Derecho (Title of Licentiate in Law) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. |
| Título de Licenciado en Educación Preescolar / Primaria / Secundaria / Media Superior con especialidad en xxx (Title of Licentiate in Preschool / Primary / Secondary Education / Upper Secondary Education with specialization in xxx) | Completion of Grade 12: Certificado de Bachillerato (Certificate of Baccalaureate) Titulo de Maestro / Profesor de Educación Preescolar / Educación Primaria (Title of Preschool / Primary School Teacher): advanced standing | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor of Education degree. |
| Diploma de Especialidad (Diploma of Specialist) | Titulo de Licenciado (Title of Licentiate) | 1 year | Generally compares to the completion of a graduate diploma. |
| Grado de Maestria (Master’s Degree) | Titulo de Licenciado (Title of Licentiate) Diploma de Especialidad (Diploma of Specialist): advanced standing | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| Grado de Doctor (Doctorate Degree) | Grado de Maestria (Master’s Degree) Titulo de Licenciado (Title of Licentiate): additional requirements | 3 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
Additional resources
- SEP search directory of Mexican institutions
- AUNIES search directory of higher education institutions
- RVOE search directory of private education programs
- RODAC online validation of academic credentials
- SEP online validation of professional licenses
- WENR Country Profile: An Overview of Education in Mexico