Government mail service may be affected by the Canada Post labour disruption. Learn about how critical government mail will be handled.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: Republic of Korea
Location: East Asia
Capital: Seoul
Area: 98,190 square km
Population: 48.6 million (2008 Korean Overseas Information Service)
Ethnicity: Except for a small minority of ethnic Chinese (approximately 20,000), the Korean population is homogeneous.
Religion: According to a 1995 survey, just over 50% of Koreans profess religious affiliation. Of those, 46% are Buddhists; 39% are Protestants and 13% are Catholics.
Languages: Korean is both the official language and the language of instruction in Korea.
Founding Date: The Republic of Korea was established on August 15, 1948, after the United States and the former Soviet Union divided the Korean peninsula into North and South Korea.
Government and Administration: South Korea is a republic governed by a directly elected president and a unicameral legislature, the National Assembly. Currently there are 16 provincial-level governments (9 provinces and 7 provincial-level metropolitan cities) and 235 lower-level local governments.
School education
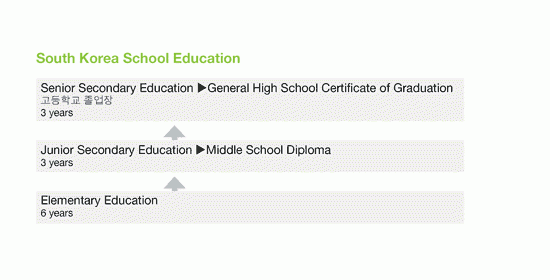
South Korea has adopted a 12-year system of school education, consisting of 6 years of primary education, 3 years of junior secondary education and 3 years of senior secondary education. Upon completion of senior secondary school, students are awarded the General High School Certificate of Graduation 인문계 고등학교 졸업장, which gives access to university study.
Higher education overview

Higher education in South Korea follows the 3-tier degree structure – bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral-level studies. In addition, junior college diplomas and associate degrees are offered at undergraduate levels.
General bachelor’s degree 학사 학위 programs, such as the Bachelor of Arts and Bachelor of Science, involve 4 years of full-time study. Professional bachelor’s degrees in specialized fields such as medicine and dentistry take 6 years to complete.
Master’s degree 석사 학위 programs involve 2 years of study, including a thesis, beyond the bachelor’s degree.
Doctoral degree 박사 학위 (PhD) programs may be administered separately or integrated with master’s degree programs. Students must complete 36 credit hours of coursework or 60 credit hours in combination with the master’s degree. It takes at least 2 years to complete coursework and a total of 3 or more years to complete the entire doctoral program.
Technical education
Technical/vocational education may be introduced in secondary school (leading to the Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation) and continues into further and higher education.
A Diploma or Associate Degree 전문대학 졸업장 awarded by a junior college typically requires 2 to 3 years of study. Graduates may seek certification or further education. In some fields, holders of a diploma or associate degree may take a 2-year bridging program to complete a bachelor’s degree.
Institutions
Currently there are 9 major categories of higher education institutions:
- colleges and universities
- industrial universities
- junior colleges
- air and correspondence universities (open universities)
- technical colleges
- miscellaneous institutions
- cyber universities
- graduate schools
Since 1992, the Korean Council for University Education (KCUE) has been responsible for the evaluation and accreditation of educational programs in all 4-year colleges and universities, conducting assessments at departmental and institutional levels.
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| 인문계 고등학교 졸업장 (General High School Certificate of Education) | Completion of Middle School (9 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| 실업계 고등학교 졸업장 (Vocational High School Certificate of Education) | Completion of Middle School (9 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma, including vocational study. |
| 전문대학 졸업장 (Diploma / Associate Certificate of Graduation / Junior College Diploma) | General or Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation (12 years) | 2 to 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 2- or 3-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| 학사 학위 (Bachelor’s degree) | General or Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation (12 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| 의학사 (Bachelor of Medicine) | General or Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation (12 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine. |
| 치과의학사 (Bachelor of Dentistry) | General or Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation (12 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in dentistry. |
| 한의학사 (Bachelor of Oriental Medicine) | General or Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation (12 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a Bachelor’s degree with a focus in oriental medicine. |
| 수의학사 (Bachelor of Veterinary Medicine / Doctor of Veterinary Medicine) | General or Vocational High School Certificate of Graduation (12 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in veterinary medicine. |
| 석사 학위 (Master’s degree) | Bachelor’s degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| 경영학 석사 (Master of Business Administration) | Bachelor’s degree | 2 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a Master of Business Administration degree. |
| 박사 학위 (Doctoral degree) | Master’s degree | 3 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
Full credential templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in South Korea.
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English translation (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compares to educational standards in Alberta
South Korea - credential templates
Additional resources
- Ministry of Education, higher education
- Korea Polytechnics
- Korea Institute for Curriculum and Evaluation
- Korea Research Institute for Vocational Education and Training
- Korean Council for College Education
- Korean Council for University Education
- Korean Culture and Information Service