Government mail service may be affected by the Canada Post labour disruption. Learn about how critical government mail will be handled.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: Republic of the Philippines
Location: Southeast Asia
Capital: Manila
Area: 300,179 square km
Population: 100.9 million (2015 census)
Ethnicity: 95% of the population is Malay. The Chinese, representing approximately 2% of the population, are the largest minority group.
Religion: Catholicism is the predominant religion in the Philippines, counting roughly 80% of the population as adherents. The remainder of the population is divided amongst Islam, Protestant Christianity and other sects and religions. Islam is especially prevalent in the Mindanao region.
Languages: Filipino and English are the 2 official languages of the Philippines. English is the language of instruction in most subjects in all levels of education. Over 100 regional languages are also spoken in the Philippines.
Founding Date: The Philippines was under Spanish control for 3 centuries, followed by roughly 50 years of American dominion. The independent Republic of the Philippines was officially inaugurated on July 4, 1946.
Administration: The country follows a democratic system of government. The Philippines is subdivided into 17 administrative regions.
School education
Since the 1940s, the Philippines has followed a 10 year system of school education, consisting of 6 years of primary school and 4 years of secondary school. Following completion, students were awarded a High School Diploma which would grant access to university. In 2012, the K to 12 reform changed compulsory basic education to include kindergarten, 6 years of primary school, and 6 years of secondary school. The expanded secondary school is subdivided into 4 years of junior high school and 2 years of senior high school. In 2016, senior high school was implemented nationwide. Upon successful completion of senior high school, students receive a Senior High School Diploma (Katibayan). The completion of senior high school gives access to university study.
Higher education overview

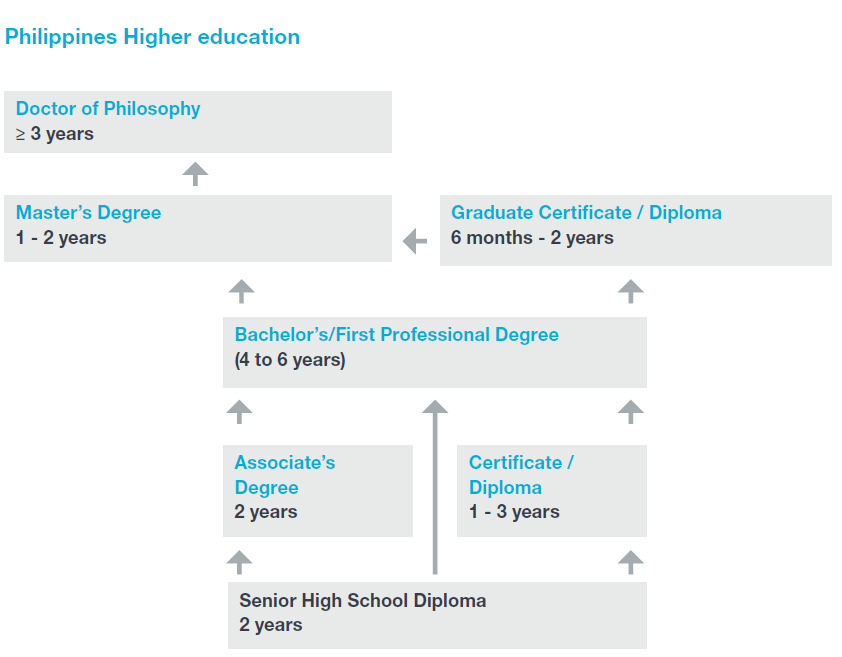

Higher education in the Philippines has been heavily influenced by the American system and typically follows a 3-tier degree structure – bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral-level studies. Although an Associate's degree may be awarded as a first degree. Certificate and diploma programs are also offered at both the undergraduate and graduate levels.
Admissions Based on the High School Diploma (10 Years) (Until 2016)
Associate degrees typically involve 2 years of study, although some may take 3 years.
Bachelor’s degrees are the most common first degree awarded. General bachelor’s degrees involve 4 years of full-time study. Bachelor’s degrees in specialized and professional fields such as engineering require 5 years. First professional degrees in dentistry, optometry and veterinary medicine typically require 6 years. Degrees in medicine and law require at least 4 years following the completion of a relevant Bachelor's degree.
Master’s degrees, which may be either research-based or professional, require 2 years of full-time study beyond the bachelor’s degree. Many graduate students attend part-time, and must complete their degrees within 5 years.
Doctoral degrees, may be either research-based or professional and normally require 5 years of study after the Master’s degree. They can be completed in as few as 3 years but must be completed within a maximum of 8 years of study.
Admissions Based on the Senior High School Diploma (12 Years) (Since 2018)
The Philippine Qualifications Framework (PQF) has eight levels of qualifications. Senior High School representing 12 years of education is the foundation of the qualifications framework. The Commission on Higher Education’s (CHED) guidelines for bachelor degree programs have been revised significantly, especially following the full implementation of the K to 12 reform. General and specialized bachelor’s degree programs involve 4 years of full-time study. First professional degrees in dentistry, optometry and veterinary medicine require 6 years; and degrees in medicine and law require at least 4 years, following the completion of a relevant Bachelor’s degree. Research-oriented and professional graduate degrees are being revised accordingly.
Technical education
Credentials obtained through technical / vocational education programs are identified by a variety of titles chosen by the institution or program, including diploma, associate, graduate or certificate. The duration of these programs varies – they can be as short as 30 hours or up to 3 years in length. Students who have completed the appropriate qualification requirements may sit the National Certificate examinations.
Institutions
In the Philippines, private higher education institutions are the most common. Although public schools represent only 10% of the total number of institutions, they enrol almost a third of all students pursing higher education. Since 1994, the Commission on Higher Education (CHED) has administered and supervised all tertiary-level, degree-granting institutions in both the private and public sectors. CHED provides a Directory of Higher Education Institutions.
The Technical Education and Skills Development Authority (TESDA) approves individual technical and vocational education programs, rather than institutions. TESDA maintains a list of approved programs on its website.
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
Katibayan or Katunayan (sekundarya) (High School Diploma) (10 years) The last cohort of completers was in 2016. | Completion of Elementary School (6 or 7 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Certificate of High School Achievement. |
| Katibayan or Katunayan (Senior High School Diploma) (12 years) | Completion of Junior Secondary School or Grade 10 (4 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| Sertipiko or Diploma (Certificate or Diploma (1-year post-secondary program)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 1 year | The combination of the High School Diploma and a 1-year Certificate or Diploma generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma, including vocational / or technical / or professional training. |
| Sertipiko or Diploma (Certificate or Diploma (2-year post-secondary program)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 2 years | The combination of the High School Diploma and a 2-year Certificate or Diploma generally compares to the completion of a 1-year post-secondary Certificate. |
| Sertipiko or Diploma (Certificate or Diploma (3-year post-secondary program)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 3 years | The combination of the High School Diploma and a 3-year Certificate or Diploma generally compares to the completion of a 2-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| Asoyado (Associate’s degree (2-year program)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 1-year post-secondary Certificate. |
| Asoyado (Associate’s degree (3-year program)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 1-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| Batsilyer (Bachelor’s degree) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a three-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Batsilyer (Teraping Okupasyonal / Terapiya Pisikal) (Bachelor’s degree (Occupational Therapy / Physical Therapy)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 5 years, including 1 year of internship | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Batsilyer (Inhenyeriya / Arkitektura) (Bachelor’s degree (Engineering / Architecture)) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Doktor ng Medisina (Doctor of Medicine) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine. |
| Doktor ng Medisinang Dental (Doctor of Dental Medicine) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in dentistry. |
| Doktor ng Optomitrya (Doctor of Optometry) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in optometry. |
| Doktor ng Panggagamot sa Hayop (Doctor of Veterinary Medicine) | High School Diploma (10 years) | 6 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in veterinary. |
| Batsilyer sa Pambabatas (LLB) or Batsilyer sa Batas (Bachelor of Laws, Juris Doctor) | Bachelor's degree | 4 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. |
| Postgradweyt Sertipiko or Diploma (Postgraduate Certificate or Diploma) | Bachelor’s degree | 0.5 year to 2 years | Assessed individually depending upon duration and the type of courses taken. |
| Masterado, Dalubhasa, Kadalubhasan (Master’s degree) | Bachelor’s degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| Master sa Pangangasiwa sa Negosyo (Master of Business Administration) | Bachelor’s degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master of Business Administration degree |
| Master (Pamamahala / Pamamahalang Pangmadla / Pamamahala sa Kalakal) (Master (Management / Public Administration / Business Management)) | Bachelor’s degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master of Management degree / Master of Public Administration degree / Master of Business Management degree |
| Doktor sa Pilosopiya (Doctor of Philosophy degree) | Master’s degree | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
Full credential templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in the Republic of Philippines.
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English translation (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compares to educational standards in Alberta
Republic of Philippines - credential templates
Additional resources
- Commission on Higher Education
- Technical Education and Skills Development Authority
- Department of Education
- National Statistics Office
- Professional Regulation Commission
- UNESCO International Bureau of Education