Government mail service may be affected by the Canada Post labour disruption. Learn about how critical government mail will be handled.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: Islamic Republic of Pakistan
Location: South Asia
Capital: Islamabad
Area: 800,000 square km
Population: 184.4 million (2010 estimate: CIA Factbook
Ethnicity: Pakistan has a number of ethnic groups, with each of the 4 provinces having 1 numerically dominant ethno-linguistic group. The population is: 45% Punjabi, 15% Pashtun, 14% Sindhi, 8% Seraiki, 8% Muhajir, and 4% Balochi, amongst others.
Religion: Over 96% of Pakistanis are Muslim, with the large majority being Sunni. There are also small minorities of Hindus (1.6%) and Christians (1.6%).
Languages: While only a small minority of the population speak Urdu as their first language, it is the national language of Pakistan. English also has official status and is widely used, along with Urdu, in government and commerce. Urdu is the language of instruction in secondary and higher secondary school. Both Urdu and English are languages of instruction in higher education.
Founding Date: Pakistan was established in August 1947 when British-ruled India gained independence and was partitioned into India and Pakistan. Founded as the Dominion of Pakistan, it was renamed the Islamic Republic of Pakistan in 1956. It initially consisted of 2 parts, West Pakistan and East Pakistan, divided by 1,600 kilometres of Indian Territory. In 1971, East Pakistan seceded and became the independent nation of Bangladesh.
Administration: Pakistan is a federal republic, with 4 provinces, 1 territory and 1 capital territory.
School education

Pakistan has adopted a 12-year system of school education consisting of 8 years of elementary education (primary and middle school), 2 years of secondary education, and 2 years of higher secondary/intermediate education.
Students in Class 10 and Class 12 take external examinations conducted by 1 of the 26 public examination bodies to receive their exit credentials. The credential representing the completion of secondary education is the Secondary School Certificate (SSC), also known as Matriculation Certificate. The credential representing the completion of higher secondary education is the Higher Secondary Certificate (HSC), also known as Intermediate Examination Certificate. The completion of higher secondary education gives access to university study.
Higher education overview
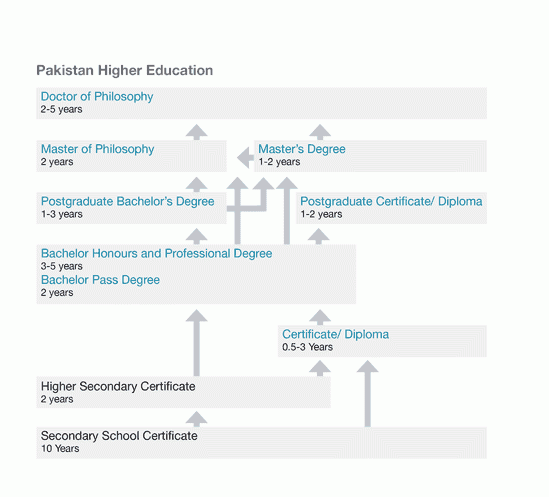
Higher education in Pakistan follows the 3-tier degree structure (bachelor’s, master’s and doctoral-level studies). In addition, there are certificate and diploma programs at both the undergraduate and graduate levels.
Bachelor (pass) degrees such as the Bachelor of Arts (BA), Bachelor of Commerce (B.Com) and Bachelor of Science (B.Sc.), traditionally involve 2 years of full-time study. Bachelor (honours) degrees typically involve 3 years of full-time study. Unlike 2-year degrees, these programs usually have areas of specialization, such as BA (English), BA (Philosophy), B.Sc. (Geology), B.Sc. (Forestry), etc. Professional bachelor’s degrees in specialized areas such as engineering and agriculture are traditionally 4 years in length.
Upgraded bachelor (honours) degrees are recently-implemented, 4-year degrees following the North American pattern. The 4-year bachelor’s degrees are considered equivalent to traditional general master’s degrees for purposes of employment and further education.
Postgraduate bachelor’s degrees require the completion of a previous bachelor’s degree for admission. These are offered in a few specialized or professional fields such as education, library science and law.
Master’s degrees involve 2 years of full-time study following a bachelor’s (pass) degree, or 1 year of full-time study following a bachelor’s (honours) degree. Master’s degrees in professional fields involve 3 to 4 semesters of full-time study following a bachelor’s degree in the same or a related field, as do master’s degrees that follow a 4-year bachelor’s degree.
Master of Philosophy (MPhil) degrees involve 2 years of full-time study following a master’s degree or a 4-year bachelor’s degree.
Doctoral degree (PhD) programs last at least 2 years after an MPhil or 3 years after a master’s degree.
Technical education
Diploma courses in various technical fields last between 6 months and 4 years following the completion of either Class 10 or Class 12. For example, a Diploma of Associate Engineer requires 3 years of study following the Secondary School Certificate. The Diploma in General Nursing is a 3-year program following the Higher Secondary Certificate.
Institutions
The 2 types of institutions are authorized to award academic degrees in Pakistan: universities and other degree-awarding institutions. Although they offer both undergraduate and graduate programs, their focus is on graduate education and research, with undergraduate teaching mostly conducted at affiliated colleges.
The Higher Education Commission provides a list of recognized universities and degree-awarding institutions. The Provincial Boards of Technical Education (Punjab, Sindh and Khyber Pakhtunkhwa) conduct major examinations and issue technical certificates and diplomas.
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Secondary School Certificate | Completion of Elementary and Middle School (8 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of Grade 10. |
| Higher Secondary Certificate | Secondary School Certificate (10 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| Diploma of Associate Engineer | Secondary School Certificate (10 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Certificate. |
| Bachelor’s (Pass) degree (2-year program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 2-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| Bachelor’s (Honours) degree (3-year program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 3-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Bachelor’s (Honours) degree (4 or 5-year program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 4 or 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor's degree. |
| Bachelor of Technology (Pass) degree (1 year of academic study) | Diploma of Associate Engineer | 1 year | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. |
| Bachelor of Technology (Pass) degree (2 years of academic study) | Diploma of Associate Engineer | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 3-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| Bachelor of Technology (Honours) degree (2 years of academic study in total) | Bachelor of Technology (Pass) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 3-year post-secondary Diploma. Note: In combination with the Bachelor of Technology (Pass) degree. |
| Bachelor of Technology (Honours) degree (3 or more years of academic study in total) | Bachelor of Technology (Pass) | 3 or more years | Generally compares to the completion of an applied Bachelor's degree. Note: In combination with the Bachelor of Technology (Pass) degree. |
| Bachelor of Education (1-year program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 1 year | Generally compares to the completion of a 3-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in education (when assessed separately) or with a focus in xxx and education (when combined with a 2-year Bachelor (Pass) degree). |
| Bachelor of Education (3 -year integrated program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 3-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in education. |
| Bachelor of Education (4-year upgraded program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in education. |
| Bachelor of Laws (2-year program) | Completion of a Bachelor’s degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. Note: These degrees were issued prior to 1992. |
| Bachelor of Laws (3-year after-degree program) | Completion of a Bachelor’s degree | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. |
| Bachelor of Laws (5-year integrated / consolidated program) | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. |
| Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine. |
| Bachelor of Dentistry / Bachelor of Dental Surgery | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in dentistry. |
| Doctor of Veterinary Medicine | Higher Secondary Certificate (12 years) | 4 or 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in veterinary medicine. |
| Master’s degree (1 or 2-year program) | Bachelor's (Pass) degree or Bachelor’s (Honours) degree | 1 or 2 years | (In combination with the preceding bachelor's degree) Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Master of Education (1-year program) | Bachelor of Education degree (1-year program) | 1 year | [In combination with 1-year BEd] Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in xxx and education. |
| Master of Education (2-year program) | Bachelor of Education degree (4-year upgraded program) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree with a focus in education. |
| Master of Arts in Education | Bachelor’s (Pass) degree or Bachelor’s (Honours) degree | 1 or 2 years | [In combination with the preceding bachelor’s degree] Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in xxx and education. |
| Master of Philosophy | Master’s degree | 1.5 to 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| Doctor of Philosophy | Master of Philosophy | 3 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. Note: Prior to May 31, 2005 the minimum admission requirement was a general Master’s degree representing at least 16 years of education. |
Full credential templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in the Islamic Republic of Pakistan
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English translation (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compares to educational standards in Alberta
Islamic Republic of Pakistan - credential templates
Additional resources
- Government of Pakistan
- Higher Education Commission
- Institute of Chartered Accountants of Pakistan
- Institute of Cost and Management Accountants of Pakistan
- Inter Board Committee of Chairmen
- Khyber Pakhtunkhwa Board of Technical Education
- Pakistan Medical and Dental Council
- Sindh Board of Technical Education