Government mail service may be affected by the Canada Post labour disruption. Learn about how critical government mail will be handled.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: Republic of Colombia
Location: South America
Capital: Santa Fe de Bogotá
Area: 1.1 million square km
Population: 43 million (2005 census
Ethnicity: The ethnic makeup of present-day Colombia reflects its rich heritage. The population is estimated to be 58% Mestizo, 20% White and 14% Mulato. The remaining 8% of the population is Black, Amerindian or a mixture of the two.
Religion: Catholicism plays an important role in Colombia, where it was once an official state religion. About 90% of Colombians are Catholic. Most major religions and religious movements are also present in the country.
Languages: Spanish is the official language and the primary language of instruction in Colombia; however the indigenous languages of several ethnic groups are constitutionally recognized, and bilingual education is a legal obligation in regions with a linguistic tradition of their own.
Founding Date: Colombia declared its independence from the Spanish crown on July 20, 1810. In 1830, Venezuela and Ecuador separated from Greater Colombia. In 1886, the current Republic of Colombia was established, though Panama became a separate nation in 1903.
Administration: Colombia is a republic; the executive branch dominates the government structure. It is administered by 32 departments and 1 capital district.
School education
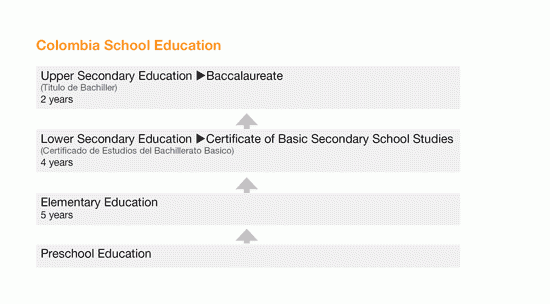
The Republic of Colombia follows an eleven year system of school education, consisting of 5 years of elementary education, 4 years of lower secondary education and 2 years of upper secondary education. At the end of upper secondary school, students are awarded the title of Baccalaureate (Titulo de Bachiller), which gives access to university study. The actual name of the credential may vary, and on the certificate, Bachiller may be preceded by Titulo de..., Diploma de... or Grado de....
Higher education overview
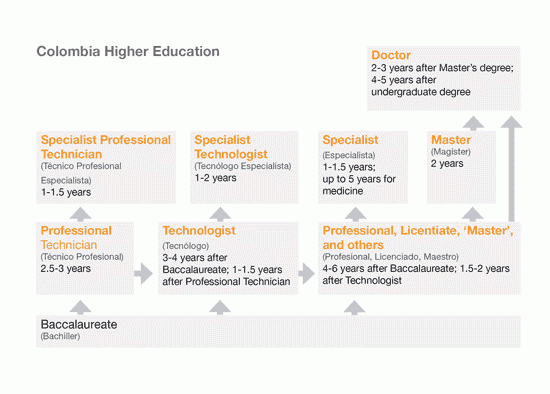
Higher education in Colombia follows a 3-tier degree structure – undergraduate, graduate and doctoral level.
Professional title (título professional) undergraduate programs involve 4 to 5 years of full-time study. Although an undergraduate degree in Colombia is normally referred to as a professional title, the exact name of the degree can vary depending on the discipline (i.e. Profesional en ..., Licenciado en..., Maestro en ... and Titulo de…). Undergraduate degrees in professional fields such as dentistry, engineering, law and veterinary medicine typically require 5 years of full-time study, while medicine requires 6 years.
Specialist (titulo de especialista) programs involve one to one-and-a-half years of full-time study following an undergraduate degree; though specializations in health care professions may last up to 5 years. Specializations at this level are usual in professions associated with medicine, law and business administration. Those who choose to enter a program leading to the titles of master or doctor are not generally given any transfer credit for studies completed at the specialization level.
Master’s programs (titulo de magister) involve 2 years of study and require the completion of an undergraduate degree for admission. Master’s students must prepare and defend a comprehensive research project in order to graduate.
Doctoral programs (titulo de doctor) last 4 to 5 years if taken immediately after an undergraduate degree, or an additional 2 to 3 years if taken after a master’s degree in the same field. Doctoral candidates are required to complete and defend a thesis that represents an original contribution to their field of study.
Technical education
Upper secondary graduates may also pursue technical education by taking a 2-and-a-half to 3 year program leading to a professional technician title (tecnico profesional). Professional technicians may take a further one to one-and-a-half years of specialization, leading to the title of specialist professional technician (tecnico profesional especialista).
A title of technologist (titulo de tecnólogo) program lasts 3 to 4 years and is available to holders of either a titulo de bachiller or a tecnico profesional. Title of technologist holders may study for an additional one to 2 years to receive a specialist technologist title (tecnólogo especialista). The combination of a technologist title and a specialist technologist title is regarded in Colombia as comparable to an undergraduate degree.
Institutions
Currently, higher education consists of the following types of institutions: professional technical institutions, technological institutions, technological schools, university institutions and universities. The most important characteristic that sets the universities apart from other post-secondary institutions is the emphasis on research activities.
The obligatory licensing of institutions and registration of programs should not be confused with accreditation, which is voluntary in Colombia. An institution can be fully authorized to offer a non-accredited program. The National System of Accreditation (Sistema Nacional de Acreditación), maintains a searchable online database of information about all registered higher education institutions and programs.
Accreditation is awarded on a program-by-program basis, starting at the undergraduate level. The CNA maintains a list of all accredited programs. The ultimate level of accreditation pertains to the entire institution and is separate from the accreditation of individual programs.
Credential comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Titulo de Bachiller (Title of Baccalaureate) | Completion of Elementary and Lower Secondary School (9 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| Titulo de Tecnico Profesional (Title of Professional Technician) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 2.5 to 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Certificate. |
| Titulo de Tecnico Profesional Especialista (Title of Specialist Professional Technician) | Title of Professional Technician | 1 to 1.5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Post-secondary Certificate. |
| Titulo de Tecnólogo/a (Title of Technologist) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. |
| Titulo de Tecnólogo/a Especialista (Title of Specialist Technologist) | Title of Technologist | 1 to 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. |
| Titulo de Normalista Superior (Title of Preschool and Elementary Teacher) | Title of Baccalaureate specializing in education (11 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. |
| Titulo de Profesional, Licenciado/a, Maestro/a (Title of Professional, Licentiate, Master and other Undergraduate degree Titles) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 4 to 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Titulo de Odontologo/a (Title of Dentist) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in dentistry. |
| Titulo de Ingeniero/a (Title of Engineer) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor's degree. |
| Titulo de Abogado/a (Title of Lawyer) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. |
| Titulo de Medico or Medico y Cirujano (Title of Physician or Physician and Surgeon) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 6 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine. |
| Titulo de Enfermero/a (Title of Nurse) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 4 to 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor's degree. |
| Titulo de Terapeuta Ocupacional or Titulo de Fisioterapeuta (Title of Occupational Therapist or Physical Therapist) | Title of Baccalaureate (11 years) | 4 to 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a 4-year Bachelor's degree. |
| Titulo de Medico Veterinario (Title of Veterinarian) | Title of Bachiller, i.e., completion of Grade 11 | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in veterinary medicine. |
| Titulo de Especialista (Title of Specialist) | Undergraduate degree | 1 to 1.5 years and up to 5 | Generally compares to the completion of a graduate Diploma. |
| Titulo de Magister (Title of Master) | Undergraduate degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| Titulo de Magister en Administracion de Empresas (Title of Master of Business Administration) | Undergraduate degree | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master of Business Administration degree (MBA). |
| Titulo de Doctor (Title of Doctor) | Undergraduate degree in a related field; most applicants are admitted based on a Master’s degree | 2 to 3 years following a Master’s degree or 4 to 5 years following an undergraduate degree | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
Full credential templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in the Republic of Colombia
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English translation (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compares to educational standards in Alberta
Republic of Colombia - credential templates
Additional resources
- Academia Nacional de Aprendizaje
- Asociación Colombiana de Facultades de Administración
- Asociación Colombiana de Universidades
- Fundación CESDE
- Secretaría de Educación de Bogotá
- Servicio Nacional de Aprendizaje (SENA)