Non-urgent government operations are closed December 24 to January 1, reopening January 2. View available services during this period.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: People's Republic of China
Location: East Asia
Capital: Beijing
Area: 9.6 million square km
Population: 1.3 billion (2000 census)
Ethnicity: China has 56 ethnic groups, with Han Chinese making up 91% of the population.
Languages: Chinese (Hanyu) is the official language and the language of instruction. In some areas, local languages such as Tibetan and Uyghur are used, along with Chinese, as the official language and language of instruction in both school and higher education.
Founding Date: The Communist Party of China, led by Mao Zedong, defeated Kuomintang forces and proclaimed the founding of the People’s Republic of China on October 1, 1949.
Administration: China is a communist country with a strong central government. The 32 major administrative regions include 23 provinces, 5 autonomous regions, and 4 centrally administered municipalities (Beijing, Shanghai, Tianjin, and Chongqing).
School education
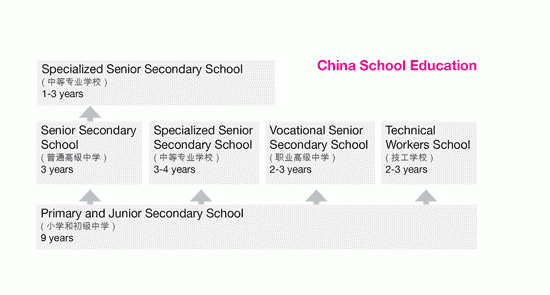
China has adopted the current 12-year school system since the early to mid-1980s. The academic stream consists of 9 years of primary and junior secondary education and 3 years of senior secondary education. The Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School gives access to university study.
Higher education overview
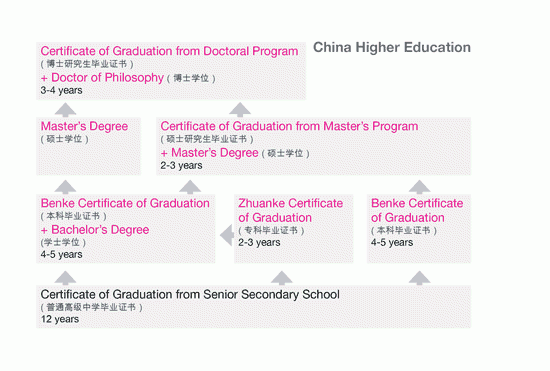
Chinese higher education awards 2 types of credentials: degrees and certificates of graduation. Like degrees, certificates of graduation are considered complete credentials and can lead to both employment and further education. Most conventional programs issue both a certificate of graduation and a degree certificate.
Zhuanke refers to post-secondary programs involving 2 or 3 years of full-time study. Zhuanke graduates may enter part-time bridging programs leading to a Bachelor’s degree.
Benke refers to undergraduate programs involving 4 to 5 years of full-time study. The majority of Benke graduates receive both a certificate of graduation and a Bachelor’s degree. Some graduates will only receive a certificate of graduation due to an academic deficiency such as failing a national English proficiency test or for non-academic reasons such as political activism.
Master’s programs typically involve 2 to 3 years of full-time study and award both a certificate of graduation and a Master’s degree. Some professional degrees and part-time programs only award a Master’s degree.
Doctoral programs usually involve 3 to 5 years of full-time study and award both a certificate of graduation and a doctoral degree.
Institutions
China has over 2,000 regular and adult higher education institutions. Regular institutions offer programs ranging from Zhuanke to Doctoral levels, while adult institutions can only operate programs at Zhuanke and Benke / Bachelor’s degree level. The majority of institutions are public. Minban (private) institutions have developed rapidly in recent years but are generally not as well regarded as public institutions.
The Ministry of Education provides lists of recognized institutions in China in both Chinese and English.
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| 普通高级中学毕业证书 高中毕业证书 (Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School) | Completion of Primary and Junior Secondary School (9 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| 中等专业学校毕业证书 中专毕业证书 (Certificate of Graduation from Specialized Senior Secondary School) | Completion of Primary and Junior Secondary School (9 years) | 3 to 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma, including vocational study. Note: This is a common pattern. |
| 中等专业学校毕业证书 中专毕业证书 (Certificate of Graduation from Specialized Senior Secondary School (1 to 2 year program)) | Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School (12 years) | 1 to 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of one or two years of vocational study. Note: This pattern was popular in the 1980s and early 1990s. |
| 专科毕业证书 专科毕业文凭 大专毕业证书 (Certificate of Graduation (2 to 3-year post-secondary zhuanke program) ) | Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School (12 years) | 2 to 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a two or three-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| 高等教育自学考试专科毕 业证书 (Certificate of Graduation (2 to 3-year post-secondary zhuanke program) through self-study) | Admission requirements vary | 2 to 3 years through self-study | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. |
| 本科毕业证书 本科毕业文凭 (Certificate of Graduation (4 to 5- year undergraduate benke program)) | Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School (12 years) | 4 to 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| 高等教育自学考试本科毕业 证书 Certificate of Graduation (4-year undergraduate benke program) through self-study | Admission requirements vary | 4 year through self-study | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. Note: This pattern is very rare. |
| 专升本毕业证书 大专后毕业证书 (Certificate of Graduation (2-year university upgrading benke program)) | Certificate of Graduation (2-3 year post-secondary program) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| 高等教育自学考试本科毕业 证书 (Certificate of Graduation (2-year university upgrading benke program) through self-study) | Certificate of Graduation (2 to 3 year post-secondary program) | 2 years through self-study | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. Note: This is a common pattern. |
| 学士学位 (Bachelor’s degree) | Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School (12 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| 医学学士学位 (Bachelor’s Degree in Medicine) | Certificate of Graduation from Senior Secondary School (12 years) | 5 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine. |
| 硕士学位 (Master’s degree) | Bachelor’s degree | 2 to 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| 博士学位 (Doctor’s degree) | Master’s degree | 3 years (minimum) | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
Full credentials templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in the People’s Republic of China.
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English tradition (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compared to educational standards in Alberta
People's Republic of China - credential templates
Additional resources
- Chinese Ministry of Education
- China Academic Degrees and Graduate Education Development Centre
- UNESCO International Bureau of Education. World data on education: China