Government mail service may be affected by the Canada Post labour disruption. Learn about how critical government mail will be handled.
Overview
This guide profiles the educational systems of Bangladesh. The International Qualifications Assessment Service (IQAS) branch compares credentials from these countries with educational standards in Canada, and can be used to make accurate and efficient decisions about the recognition of international credentials, it is a resource for institutions.
Download credential templates
This is not an official IQAS assessment. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They do not take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Higher Secondary Certificate (HSC) | Secondary School Certificate (SSC) | 2 years | High School Diploma |
| Diploma in technical fields | SSC | 3 years | High School Diploma plus a postsecondary certificate |
| 4 years | High School Diploma plus a postsecondary diploma | ||
| Diploma in Nursing and Midwifery | SSC | 4 years | High School Diploma plus a postsecondary diploma with a focus in nursing and midwifery |
| HSC | 3 years | Three-year postsecondary diploma with a focus in nursing and midwifery | |
| Diploma in Midwifery | HSC | 3 years | Three-year postsecondary diploma with a focus in midwifery |
| Diploma in Homeopathic Medicine and Surgery (DHMS) | SSC | 4 years plus a 6-month internship | High School Diploma plus a postsecondary Diploma with a focus in homeopathic medicine and surgery |
| General Bachelor’s (Pass) Degree (e.g., BA, BCom, and BSc) | HSC | 2 years | Postsecondary Diploma |
| 3 years | Three-year Bachelor's Degree | ||
| General Bachelor’s (Honours) Degree (e.g., BA, BCom, and BSc) | HSC | 3 years | Three-year Bachelor's Degree |
| 4 years | Four-year Bachelor's Degree | ||
| Bachelor’s Degree in Professional and Specialized Fields (e.g., agriculture, animal husbandry, architecture, engineering, and fisheries) | HSC | 4-5 years | Four-year Bachelor's Degree |
Bachelor of Education (BEd) Bachelor of Physical Education (BPEd) | 2-year Bachelor’s degree | 1 year | Three-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in education/physical education. |
| 3-year Bachelor's degree | Four-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in education/physical education. | ||
Bachelor of Education (BEd) Bachelor of Physical Education (BPEd) | HSC | 3 years | Three-year Bachelor's degree with a focus in education. |
| 4 years | Four-year Bachelor's degree with a focus in education. | ||
| Bachelor of Laws (LLB) | 2-year Bachelor’s degree | 2 years (phased out) | First professional university degree in law |
| HSC | 4 years | ||
| Bachelor of Homeopathic Medicine and Surgery (BHMS) | HSC | 5 years | Four-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in homeopathic medicine and surgery |
| Bachelor of Ayurvedic Medicine | HSC | 5 years | Four-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in Ayurvedic medicine |
| Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery (MBBS) | HSC | 5 years plus a 1-year internship | First professional university degree in medicine |
| Bachelor of Dental Surgery (BDS) | HSC | 4 years plus a 1-year internship | First professional university degree in dentistry |
| Doctor of Veterinary Medicine (DVM) | HSC | 4 or 5 years | First professional university degree in veterinary medicine |
| General Master’s Degree (e.g., MA, MCom, and MSc) – Traditional | 2-year Bachelor's Degree | 2 years | Four-year Bachelor's Degree |
| 3-year Bachelor's Degree | 3 years | ||
| General Master’s Degree (e.g., MA, MCom, and MSc) – Upgraded | 3-year Bachelor's Degree | 2 years | Master's Degree |
| 3-year Bachelor’s degree + 1 year of Master’s Preliminary Study | 1 year | ||
| Master’s Degree in Professional and Specialized Fields (e.g., agriculture, animal husbandry, architecture, engineering, and fisheries) | 4- or 5-year Bachelor’s degree | 1-2 years | Master's Degree |
| Master of Business Administration (MBA), awarded before 2007 | 2-year Bachelor’s degree | 2 years following 2-year Bachelor’s degree | Four-year Bachelor’s degree |
| Master of Business Administration (MBA), awarded since 2007 | 4-year Bachelor’s degree | 1-2 years | Master of Business Administration (MBA) degree |
| Executive Master of Business Administration (EMBA) | 2-year Bachelor’s degree | 1-1.5 years | Three-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in business administration |
| 2 years | Four-year Bachelor’s degree with a focus in business administration | ||
| 4-year Bachelor's Degree | At least 1 year | Executive Master of Business Administration (EMBA) degree | |
| Master of Philosophy (MPhil) | Master’s Degree | 1-2 years | Master's Degree |
| Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) | MPhil or Master’s Degree | At least 1 year following MPhil | Assessed on a case-by-case basis |
Country overview
Official country name: People’s Republic of Bangladesh
Location: Southern Asia, bordering the Bay of Bengal, India, and Myanmar
Capital: Dhaka
Time: GMT +6:00
Area: 148,460 square km
Population: 167.5 million (2019 statistics)
Ethnicity: Over 98 % Bengali. The government recognizes 27 ethnic groups.
Religion: Muslim (90%), Hindu (9%), and others.
Language: Bangla, also known as Bengali. English is often used in education and business but has no official status.
Founding Date: December 16, 1971. In August 1947, British-ruled India gained independence and was partitioned into India and Pakistan. Pakistan consisted of two parts, West Pakistan and East Pakistan, separated by 1,600 kms of Indian territory. In 1971, East Pakistan seceded and became the independent nation of Bangladesh.
Administration: 8 divisions – Barisal, Chittagong (Chattogram), Dhaka, Khulna, Mymensingh, Rajshahi, Rangpur, and Sylhet.
School education
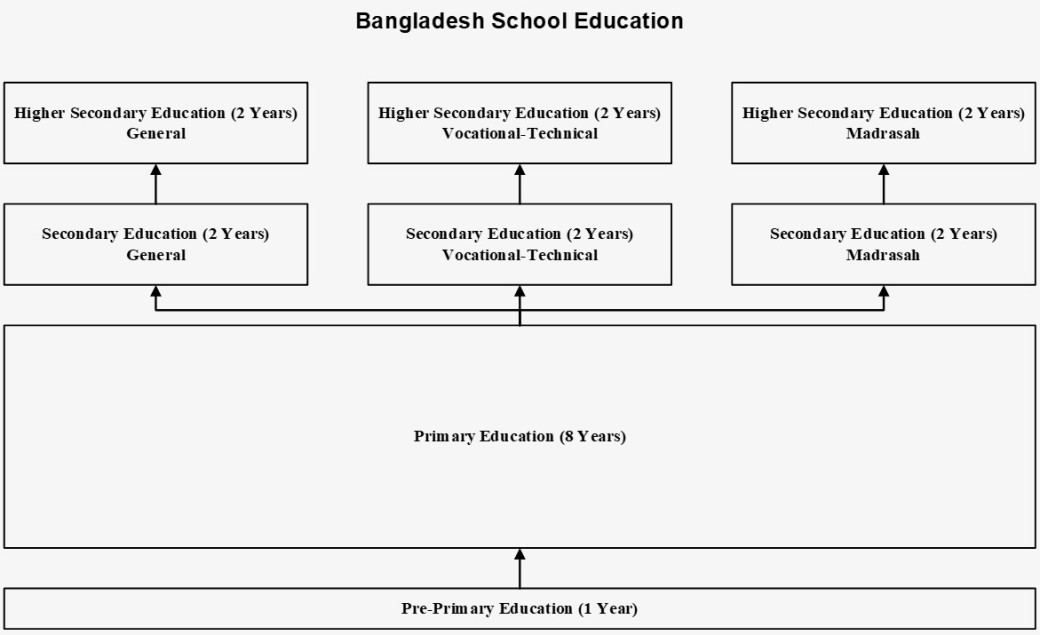
Bangladesh has a 12-year school system consisting of primary, secondary, and higher secondary education.
- Older system: 5 (primary) +5 (secondary) + 2 (higher secondary)
- Current system: 8 (primary) + 2 (secondary) + 2 (higher secondary)
Pre-primary education is not compulsory and does not have uniform curriculum standards. The national education policy of 2010 proposed one year of pre-primary education for children at age 5. Children start primary education at age 6.
The Ministry of Primary and Mass Education oversees primary education (Grades 1-8), which is compulsory and tuition-free.
The National Curriculum and Textbook Board is responsible for grade school education curriculum development. Medium of instruction is Bangla, though some private schools teach in English.
The school year is approximately 37 weeks from January to December. Students attend schools for 5 days a week (Sunday to Thursday) starting in 2023; they previously studied for 6 days a week (Saturday to Thursday). Schools may lose substantial instructional time due to natural disasters and administrative and logistic processes.
Compulsory subjects in primary education include Bangla, English, Bangladesh studies, mathematics, social environment, natural environment, religious studies, and moral science. In addition, pre-vocational training is available in Grades 6 to 8, as many primary school graduates go into employment.
The Ministry of Education oversees secondary education (Grades 9-12), which has 3 streams: general, madrasah, and vocational-technical. Compulsory subjects for all students include Bangla, English, Bangladesh studies, general mathematics, and information technology.
Secondary school students sit 2 public examinations, on the completion of Grade 10 and Grade 12 respectively. The intermediate and secondary education boards, madrasah board and technical board conduct the examinations and issue Secondary School Certificates for completing Grade 10 and Higher Secondary Certificates for completing Grade 12.
Private schools preparing students for “O” level and “A” level examinations form a special part of the general stream. The government considers the “O” and “A” levels to be equivalent to SSC and HSC respectively, if school curriculum includes Bangla and Bangladesh studies.
Higher education
The University Grants Commission (UGC), established in 1972, is the statutory body responsible for the university education sector.
The first university in Bangladesh, the University of Dhaka, was founded in 1921 during the British rule of the Indian subcontinent. The country had 6 universities at the time of independence in 1971. Private universities emerged after the Private Universities Act of 1992. The UGG publishes a Universities of Bangladesh list. Vast numbers of students in the country study at affiliated colleges of the National University.
The academic year lasts from January to December or September to August.
The medium of instruction is Bangla. Programs in science, medicine, and healthcare typically teach in English.
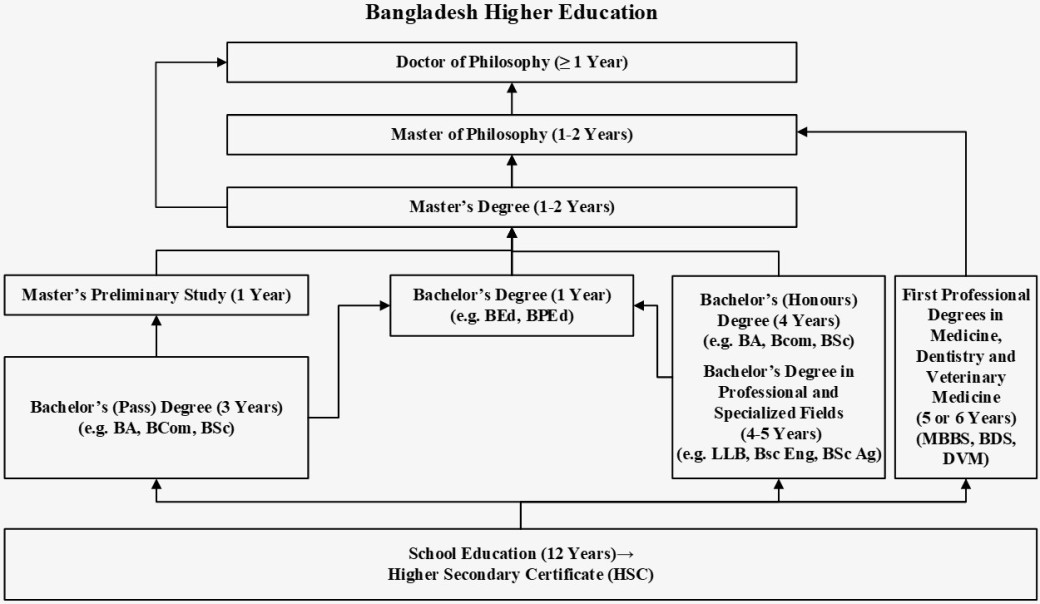
Major higher education credentials include bachelor’s (pass) degree, bachelor’s (honours) degree, master’s degree, Master of Philosophy, and doctoral degree.
General bachelor’s degrees, usually offered in 3 main categories of arts, science and commerce, may be earned as a bachelor’s (pass) or bachelor’s (honours) degree. Until around 2003-2006, the bachelor’s (pass) degree lasted 2 years, and the bachelor’s (honours) degree, three years. Currently, the bachelor’s (pass) and the bachelor’s (honours) degrees last 3 and 4 years respectively. General bachelor’s degrees typically follow the annual system, with students studying a few subjects each year and sitting annual examinations.
Some universities offer American-style 4-year bachelor’s degrees, for example Bachelor of Business Administration, that require about 120 semester credits of general and specialized subjects and the completion of a graduation thesis or project.
Professional bachelor’s degrees involve 4 or 5 years of fulltime study. Examples include agriculture, animal husbandry, architecture, engineering, fisheries, and law. First professional degrees in medicine (Bachelor of Medicine and Bachelor of Surgery), dentistry (Bachelor of Dental Surgery) and veterinary medicine (Doctor of Veterinary Medicine) last 5 or 6 years.
Some bachelor’s degrees, known as graduate entry degrees, require a first bachelor’s degree (pass or honours) for admission, for example 1-year Bachelor of Education, 1-year Bachelor of Physical Education, and 2-year Bachelor of Laws degrees.
General master’s degrees, usually offered in the 3 main categories of arts, science and commerce, last 2 years after a bachelor’s (pass) degree or one year after a bachelor’s (honours) degree. Professional master’s degrees (for example, in agriculture, animal husbandry, architecture, engineering, fisheries, and law) involve 1 to 2 years of fulltime study, with entry based on a bachelor’s degree in the same field.
The Master of Philosophy (MPhil) lasts 1 to 2 years, with entry based on a master’s degree, and usually involves the completion of both coursework and a research thesis. The MPhil is the typical requirement for entry into doctoral study.
The Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) involves at least one year of fulltime study after the MPhil. Applicants with a master’s degree or equivalent may have to meet additional requirements such as several years of teaching or research experience. A PhD program may involve both coursework and research, though there are programs with no coursework requirements. Students must complete and defend a thesis based on original research, which should contribute to existing knowledge in the field.
Teacher education
Teachers of primary grades 1 to 5 must hold an HSC and pass a selection examination and interview. Minimum qualifications for female primary school teachers is the SSC, a policy introduced in 1990 to increase the percentage of female teachers and the enrolment of girls. Primary Teacher Training Institutes (about 60 in total) and Bangladesh Open University offer the one-year Certificate in Education, largely as an in-service program. The National Academy for Primary Education conducts training and research in the field of primary education and oversees the Primary Teacher Training Institutes. In government schools, primary school teachers must obtain at least a Certificate in Education within a few years of their employment. Since 2012, Primary Teacher Training Institutes have increasingly offered an 18-month Diploma in Primary Education program.
To teach Grade 6 or above, one must hold a bachelor’s degree, for example a Bachelor of Education (BEd), which can be earned as a 1-year “graduate entry degree” or as a 4-year degree. Secondary school teachers without the requisite qualification usually study for the one-year BEd through in-service training. Teachers Training Colleges conduct most of the BEd programs, with degrees issued by affiliating universities such as the National University. Universities also offer Master of Education (1-year fulltime or 2-year part time), Postgraduate Diploma in Education, Master of Philosophy (MPhil) in Education, and PhD in education programs.
Technical-vocational education
Bangladesh Technical Education Board (BTEB) supervises technical-vocational education at secondary and postsecondary (graduates with SSC or HSC) levels.
Students may enter the vocational-technical stream at secondary level (Grades 9-12) and graduate with SSC and HSC in various vocational and technical fields, for example business management, clothing and garments finishing, industrial woodworking, poultry rearing and farming, refrigeration and air conditioning, and welding and fabrication.
Diploma programs typically last 3 or 4 years, with entry based on the SSC. Applicants with the HSC may get 2 or 3 semesters of advanced standing. A 4-year diploma usually consists of 7 semesters of both general and specialized courses and 1 semester of industrial training. Diploma holders may get advanced standing when applying for bachelor’s degree programs in the same fields.
Additional resources
- Bangladesh Bar Council
- Bangladesh Medical and Dental Council
- Bangladesh Nursing and Midwifery Council
- Bangladesh Technical Education board
- Ministry of Education
- Ministry of Primary and Mass Education
- University Grants Commission