Non-urgent government operations are closed December 24 to January 1, reopening January 2. View available services during this period.
Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: Union of Soviet Socialist Republics (former USSR)
Location: Eastern Europe and northern Asia
Capital: Moscow
Area: 22.4 million square km
Population: 286.7 million (1989 census
Ethnicity: According to the 1989 census, Russians represented 51% of the population. Other ethnic groups included: Ukrainian (15%), Uzbek (6%), Byelorussian (4%), Kazakh (3%), and Azerbaijani (2%), amongst others.
Religion: 60% of the population reported being atheists in the 1989 census. Of those who reported practicing a religion, 20% identified themselves as being Russian Orthodox; 10% as Muslim; and 7% as following other Christian religions.
Languages: Russian was the official language and the language of instruction of the former USSR.
Founding Date: Following several years of civil unrest, the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics was formed in 1922. In December 1991, the USSR splintered into Russia and 14 other independent nations.
Government and Administration: The USSR was a single-party communist state, with one soviet federative socialist republic and fourteen soviet socialist republics.
School education

The USSR followed a 10 or 11-year system of education, consisting of 3 or 4 years of primary school, 5 years of lower secondary school and 2 years of upper secondary school. One notable exception was the Baltic republics, where the overall length of school education varied between 11 and 12 years. Upon successful completion of upper secondary school, students received a school-issued Certificate of Secondary Education (Аттестат о среднем образовании / Attestat o srednem obrazovanii). This credential gave access to university study.
Higher education overview
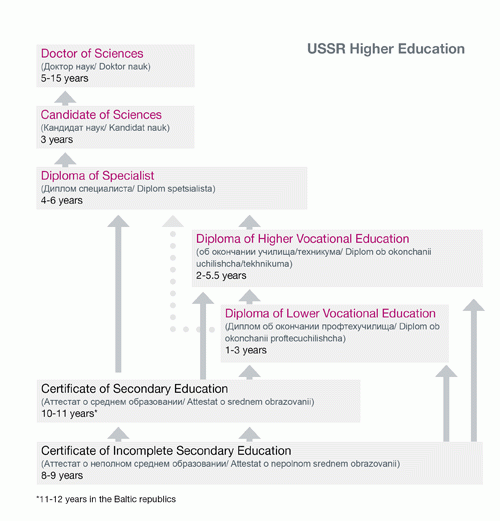
The Soviet system of higher education consisted of 2 distinct phases: a first 5-year phase, resulting in a Diploma of Specialist and a second phase of graduate studies.
The Diploma of Specialist (Диплом Специалиста / Diplom spetsialista), or First Diploma (Первый Диплом / Pervyi diplom) was the traditional first degree in the Soviet higher education system. The document itself was normally entitled Diploma of Completion of Higher Education (Диплом об окончании высшего учебного заведения / Diplom ob okonchanii vysshego uchebnogo zavedeniia) or just Diploma (Диплом / Diplom). Most specialists’ diploma programs required 5 years of full-time study, though medicine required 6 years, as did some fine arts, engineering and technology disciplines. A few disciplines, such as teaching, required 4-years of study.
The Candidate of Sciences degree (Кандидат наук / Kandidat nauk) was the first graduate degree offered in the USSR. It was a research-based program that required a minimum of 3 years of study involving coursework and a supervised thesis.
The Doctor of Sciences (Доктор наук / Doktor nauk) was a highly research-focused program for senior scholars that typically required 5 to fifteen years of full-time study following the Candidate of Sciences. A thesis and the publication of 10 to 20 scientific papers were required.
Technical education
Formal Technical and Vocational Education programs in the Russian Federation are offered at both the secondary and post-secondary levels.
The Diploma of Lower Vocational Education (Диплом о начальном профессиональном образовании / Diplom o nachalnom professionalnom obrazovanii) is typically referred to as the Diploma of Skilled Worker. Admission requirements vary, and students may be admitted based on the Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education or the Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education. The duration of studies varies between one and 4 years depending on the admission requirements and on whether the education incorporates complete secondary education. The Diploma of Lower Vocational Education gives access to employment; and if complete secondary education is incorporated into the studies, then the Diploma may also give access to higher education.
The Diploma of Higher Vocational Education (Диплом о среднем профессиональном образовании / Diplom o srednem professionalnom obrazovanii) and a professional title (i.e. Diploma of Technician, Diploma of Nurse and etc) are awarded to students who successfully complete the requisite coursework and state final examinations. Admission may be based on the Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education or the Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education.
The duration of studies varies between 2 and 5 years depending on the entrance requirements and on the type of educational institution attended. Graduates of higher vocational programs are entitled to apply to institutions of higher education and may receive advanced standing in relevant bachelor’s or specialist diploma programs.
Institutions
In 1991, there were 904 higher education institutions. State education in the USSR was free and administered by the State Committee for Public Education. Institutions of higher education included universities, institutes, academies, and conservatories. The types of institutions were considered equal in terms of academic standards, admission requirements and awards offered.
The National Information Centre on Academic Recognition and Mobility provides a list of current accredited institutions in the Russian Federation. However, please keep in mind that the names of institutions may have changed over the years, and that this list does not include institutions located in the other 14 independent nations.
Most lower vocational programs in the USSR were offered by either professional technical uchilischche or secondary professional technical uchilischche. Higher vocational education was offered by the following 3 types of specialized secondary institutions: tekhnikum, uchilischche, and colleges (since 1989).
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Аттестат о среднем образовании (Certificate of Secondary Education) | Completion of Primary and Lower Secondary School/ Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education ( 9 years) | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| Диплом об окончании профтехучилища (Diploma of Lower Vocational Education) | Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education (9 years) or Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education (typically without entrance exams) (10 to 11 years) | 1 to 1.5 years following a Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education; 2 to 3 years if following a Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education (3 year program typically incorporates complete secondary education) | Generally compares to the completion of vocational training. Note: Where training incorporates complete secondary education, the completion of a High School Diploma is acknowledged. |
| Диплом об окончании училища/техникума (Diploma of Higher Vocational Education) | Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education (9 years) or Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education (typically without entrance exams) (10 to 11 years) | 2 to 4.5 years if admitted with a Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education; 3 to 5.5 years if admitted with a Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education. | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. Note: Where training incorporates complete secondary education, the completion of a High School Diploma is acknowledged. |
| Диплом cпециалиста / Первый Диплом (Diploma of Specialist (4-year program)) | Certificate of Secondary Education and entrance exams (10 to 11 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Диплом cпециалиста / Первый Диплом (Diploma of Specialist (5 to 6-year program)) | Certificate of Secondary Education and entrance exams (10 to 11 years) | 5 to 6 years | Generally compares to the completion of: - a four-year Bachelor’s degree plus one year of a graduate Diploma. |
| Кандидат наук (Candidate of Sciences) | Diploma of Specialist, entrance exams and research qualifications | 3 years minimum, including research and optional coursework | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
| Доктор наук (Doctor of Sciences) | Candidate of Sciences, academic position and research qualifications | 5 to 15 years | Represents the completion of post-doctoral research. |
| Диплом об окончании училища / техникума (Diploma of Higher Vocational Education (Non-University-level teaching credential)) | Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education (9 years) or Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education (typically without entrance exams) (10 to 11 years) | 2 years if admitted with a Certificate of Completion of Secondary Education; 3.5 to 4 years if admitted with a Certificate of Incomplete Secondary Education | Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. Note: Where training incorporates complete secondary education, the completion of a High School Diploma is acknowledged. |
| Диплом cпециалиста (Diploma of Specialist (University-level teaching credentials) (4-year program)) | Certificate of Secondary Education and entrance exams (10 to 11 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a four-year Bachelor’s degree. |
| Диплом cпециалиста (Diploma of Specialist (University-level teaching credentials) (5 year program)) | Certificate of Secondary Education and entrance exams (10 to 11 years) | 5 to 6 years | Generally compares to the completion of: - a four-year Bachelor’s degree plus one year of a graduate Diploma; - a five-year combined Bachelor’s degree (such as BEd/BSc). |
| Диплом cпециалиста (Diploma of Specialist (Medicine / Dentistry)) | Certificate of Secondary Education and entrance exams (10 to 11 years) | 6 years | The Diploma of Physician / Stomatologist / Pediatrician / Hygienist, etc., generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in medicine, dentistry, etc. |
Full credential templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in the Former USSR.
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English translation (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compares to educational standards in Alberta
Former USSR - credential templates