Download guide

This is not an official IQAS assessment. The recommendations in this guide are for your information only. These credential comparisons represent common educational patterns within each country. They don’t take into account the recognition status of the institution through which a credential was obtained, the authenticity of the documentation, or the particular pattern of education followed by an individual.
Country overview
Official country name: Republic of Poland
Location: Central Europe
Capital: Warsaw
Area: 312,679 square km
Population: 38.1 million (2008 – General Statistical Office)
Ethnicity: Poland is primarily an ethnically homogenous state (96.7% of the population is Polish). There are nine national minority groups living in Poland and four officially recognized ethnic minorities.
Religion: The overwhelming majority of the Polish population is Roman Catholic (almost 90%). Eastern Orthodox and Protestant religions account for 1.6% of the population. There are smaller numbers of adherents to Judaism, Islam and Buddhism.
Languages: Polish is the official language of the country and the language of instruction. In 2005, national and ethnic minorities were officially given the right to freely use their languages for instruction.
Founding Date: The present Polish territory was established after World War II at the Yalta Conference in 1945, and sealed at the conference in Potsdam. The country’s official name, the Republic of Poland (Rzeczpospolita Polska), was established in accordance with the latest Constitution of April 1997.
Government and Administration: The Republic of Poland is a unitary state with a government based on the separation of the legislative, executive and judicial powers. There are 16 administrative divisions called provinces (województwo).
School education
The Republic of Poland currently follows a 12-year system of education, consisting of 6 years of primary school, 3 years of lower secondary school and 3 years of secondary school (general or specialized). Technical secondary education requires an additional year of study. Upon successful completion of secondary school, students receive a school-issued Certificate of Completion of … (Swiadectwo ukończenia...). Students may then sit the Matriculation Examinations. Successful candidates receive the Matriculation Certificate (Swiadectwo dojrzałości), which is required for admission to higher education.
Higher education overview
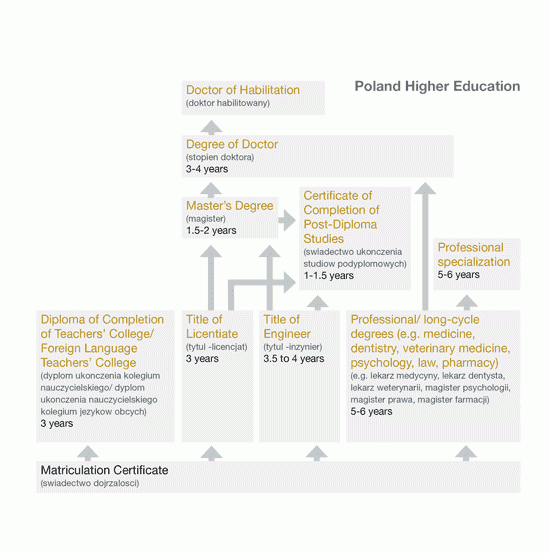
In 1992, the Republic of Poland instituted a two-cycle Licentiate / Engineer and Master’s degree system. However, the long-cycle, integrated degrees continue to be offered in primarily professional disciplines.
The Diploma of Teachers’ College / Foreign Language Teachers’ College (Dyplom ukończenia kolegium nauczycielskiego / Dyplom ukończenia nauczycielskiego kolegium jezykow obcych) involves three years of full-time study, with entry based on the completion of a Matriculation Certificate. The credentials allow an individual to seek employment as a teacher in the area of specialization, or to challenge the licentiate examinations of the affiliated university.
Holders of the Diploma of Teachers’ College may teach at the preschool or primary school level; holders of the Diploma of Foreign Language Teachers’ College may teach a foreign language at all levels of school education.
The Title of Licentiate / Title of Engineer (Tytul- licencjat / Tytul- inżynier) is the first degree in the Polish post-secondary system. Title of Licentiate degrees typically involve three years of study and Title of Engineer degrees involve three-and-a-half to four years of study. The title of Licentiate or Engineer allows its holder to practice a given profession (often after meeting additional requirements), and provides access to second-cycle (magister degree) programs.
The Master’s degree (Magister) requires three to four semesters of full-time study beyond the Licentiate / Engineer degree, depending on the field of study. Second-cycle Master’s degrees give access to doctoral studies.
Professional / Long-Cycle degree (for example: medicine, dentistry, veterinary medicine, psychology, law, pharmacy) (for example: lekarz medycyny, lekarz dentysta, lekarz weterynarii, magister psychologii, magister prawa, magister farmacji) programs last between nine and twelve semesters, depending on the field; general medicine programs being the longest.
The completion of an integrated program is considered to be at the same level as the completion of a second-cycle Master’s degree. There are eleven fields offered only as long-cycle programs: medicine, medical analysis, veterinary medicine, dentistry, law, psychology, pharmacy, film production, cinematography, acting, and art conservation / restoration studies.
Doctoral degree (Doktor) studies lead to an advanced, in-depth knowledge in a very specific discipline. They also prepare individuals to conduct independent research in the discipline studied.
The Doctor of Habilitation degree (Doktor habilitowany) is a prerequisite for appointment to senior posts in the academic profession, and ultimately leads to a title of Professor. It involves years of innovative research, several publications, and a further thesis.
Technical education
The Certificate / Diploma of Completion of Post-Lyceum Studies (Swiadectwo ukończenia szkoly policealnej/ Dyplom ukończenia szkoly policealnej) involves one to two-and-a-half years of full-time study, with entry based on the completion of secondary school. It allows an individual to seek employment or to obtain a professional qualification. The subjects studied are directly linked to the student's chosen occupation, and there is no element of general education at such schools (with the exception of physical education).
The Certificate of Completion of Post-Diploma Studies (Swiadectwo ukończenia studiow podyplomowych) typically involve one to three semesters of full-time study. They are professionally-oriented qualifications for holders of a licencjat or magister. These studies are considered to be an advantage in the labour market; however they are not considered to be either.
Institutions
Presently there are only the following two types of higher schools in the Republic of Poland: University (able to offer all levels of degree programs) and Non-university (able to offer all degree programs except at the doctoral-level).
The Ministry of Science and Higher Education provides an updated list of public and non-public institutions that were accredited following the recommendations of the State Accreditation Committee.
Credentials comparison
| Credential | Entrance requirements | Length of study | IQAS comparison |
|---|---|---|---|
| Swiadectwo ukończenia zasadniczej szkoly zawodowej (Certificate of Completion of Basic Vocational School) | Completion of Lower Secondary School (9 years) | 2 to 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of Grade Ten. |
| Swiadectwo ukończenia liceum ogolnoksztalcacego / Swiadectwo ukończenia liceum profilowanego (Certificate of Completion of General Secondary / Specialized Secondary School) | Completion of Lower Secondary School (9 years) | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Certificate of High School Achievement. |
| Swiadectwo ukończenia uzupelniajacego liceum ogolnoksztalcacego (Certificate of Completion of Supplementary General Secondary School) | Certificate of Completion of Basic Vocational School | 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Certificate of High School Achievement. |
| Swiadectwo ukończenia technikum (Certificate of Completion of Technical Secondary School) | Completion of Lower Secondary School (9 years) | 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Certificate of High School Achievement, including technical training. |
| Swiadectwo ukończenia technikum uzupelniajacego (Certificate of Completion of Supplementary Technical Secondary School) | Completion of Basic Vocational School | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Certificate of High School Achievement, including technical training. |
| Swiadectwo dojrzałości (Matriculation Certificate) | Completion of General Secondary School / Specialized Secondary School / Supplementary General Secondary School / Technical Secondary School / or Supplementary Technical Secondary School + Matriculation Examinations | n/a | Generally compares to the completion of a High School Diploma. |
| Swiadectwo / Dyplom ukończenia szkoly policealnej (Certificate / Diploma of Completion of Post-Lyceum School) | Completion of Secondary School | 1 to 2.5 years | [one-year program] Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Certificate. [at least two-year program] Generally compares to the completion of a post-secondary Diploma. |
| Tytul – licencjat/ Tytul – inżynier (Title of Licentiate/ Title of Engineer) | Matriculation Certificate | 3 to 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Bachelor’s degree. |
| Magister (Master’s Degree (2nd Cycle)) | Title of Licentiate or Title of Engineer | 1.5 to 2 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Master’s degree. |
| Magister (Master’s Degree (Integrated 1st and 2nd Cycle)) | Matriculation Certificate | 4.5 to 6 years | [fewer than 300 ECTS credits] Generally compares to the completion of a Bachelor’s degree plus a graduate Diploma. [at least 300 ECTS credits] Generally compares to the completion of a Bachelor’s degree plus a Master’s degree. |
| Dyplom – lekarza medycyny (Diploma – Doctor of Medicine) | Matriculation Certificate | 6 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional degree in medicine. |
| Dyplom – lekarza dentysta (Diploma – Doctor of Dentistry) | Matriculation Certificate | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in dentistry. |
| Dyplom – lekarza weterynarii (Diploma – Doctor of Veterinary Medicine) | Matriculation Certificate | 5.5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in veterinary medicine. |
| Magister prawa (Master in Law) | Matriculation Certificate | 5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a first professional university degree in law. |
| Doktor (Doctoral Degree) | Master’s Degree | 3 to 4 years | Generally compares to the completion of a Doctor of Philosophy (PhD) degree. |
| Doktor habilitowany (Doctor of Habilitation) | Doctoral Degree | n/a | Represents the completion of post-doctoral research. |
| Dyplom ukończenia kolegium nauczycielskiego/ Dyplom ukończenia nauczycielskiego kolegium jezykow obcych (Diploma of Completion of Teachers’ College / Diploma of Completion of Foreign Language Teachers’ College) | Matriculation Certificate | 3 years | Generally compares to the completion of a three-year post-secondary Diploma. |
| Swiadectwo ukończenia studiow podyplomowych (Certificate of Completion of Post-Diploma Studies) | Title of Licentiate, Title of Engineer, or Master’s Degree | 1 to 1.5 years | Generally compares to the completion of a university Diploma. |
Full credential templates
These templates give detailed information on educational credentials awarded for programs of study completed in the Republic of Poland.
The templates include:
- official name of credential
- alternative names
- standardized English translation (if applicable)
- time period the credential was offered
- issuing body, admission requirements into the program
- descriptive program information
- recommendations on how the credential compares to educational standards in Alberta
Republic of Poland - credential templates
Additional resources
Central Examination Commission
Conference of Rectors of Academic Schools in Poland
General Council of Higher Education
Ministry of National Education